How To Clear Cache Memory In Windows Server 2008
One of the file servers running Windows Server 2008 R2 encountered a problem of high RAM load resulting in the problems with the server and applications functioning. It turned out that the retentiveness was swamped by the system file enshroud containing file organization metadata. The problem potentially affects all file servers with large numbers of files that are accessed past users. It is the well-nigh critical for x64 Windows versions, in which the size of the metadata file in the memory can enlarge almost to the whole size of RAM.
Contents:
- High RAM Load on Windows File Server
- What is a Metafile in Windows?
- How to Speedily Clean Upwardly metafile
- Dynamic Cache Service to Manage the File Enshroud
High RAM Load on Windows File Server
The problem manifests itself every bit follows: in the Task Manager we see that physical memory is decorated by 95-99%.
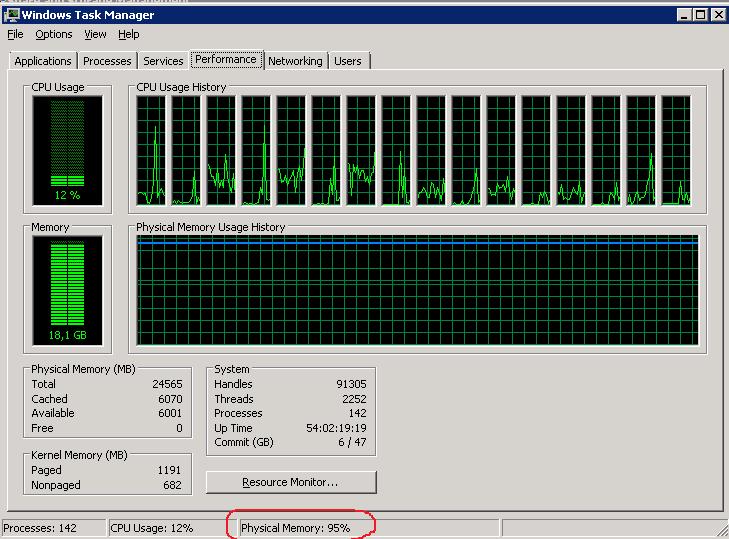
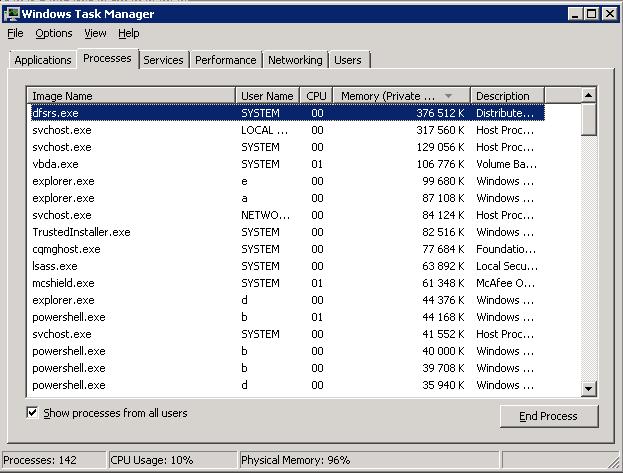
In the Processes tab, there is no whatsoever leaked process with abnormally high memory consumption. Moreover, if y'all sum the approximate values of memory used by all processes you lot won't even get 50% of physical retentiveness you take on your server. What is eating the retentiveness then?
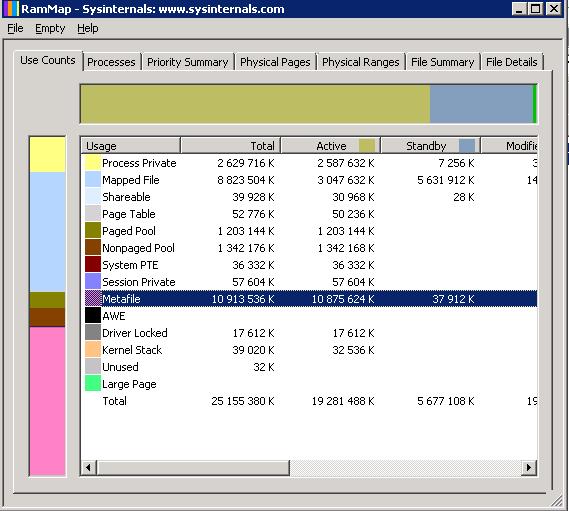
The actual data on RAM usage can be obtained with the help of small utility – RAMMap (by Mark Russinovich). Download the archive containing the tool and run RAMMap.exe with the ambassador privileges. In the Use Counts tab, nosotros see that Metafile is using the largest amount of RAM. (In our instance, it is using 11 from 25 GB of the server RAM).
What is a Metafile in Windows?
A metafile is a function of the system enshroud containing NTFS metadata and used to increase the operation of the file organization when accessing files. NTFS metadata include the data of MFT (Master File Table). For each file or folder, accessed by the users, a respective block of at least ane KB (the tape of an attribute of each file is one KB, and each file has at least one attribute) is created in the metafile. Thus, on file servers with a big number of files, the metafile size (NTFS enshroud) may exceed several tens of gigabytes.
Information technology is impossible to disable this cache or manage it using built-in Windows tools. Equally a solution, you tin increase the size of the memory on the server, but information technology is non always possible.
To gratuitous upwardly memory, you tin restart the server, but in some fourth dimension the size of the metafile in the memory starts growing incredibly.
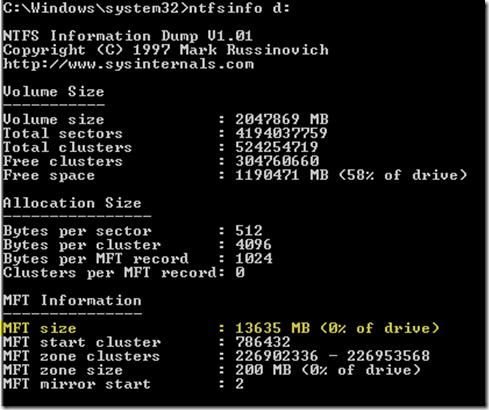
For case, y'all can estimate the size of the MFT using another tool past Russinovich – ntfsinfo. In our case, the size of the MFT on a 2 TB disk is xiii GB.
How to Quickly Clean Up metafile
RAMMap allows to quickly articulate the used memory from MFT garbage without server restart. To exercise information technology, select Empty -> Empty System Working Set in the menu.
Afterward that, the size of the metafile in the memory reduced dozens of times, and the per centum of RAM utilise by CPU dropped from 95% to 26%.
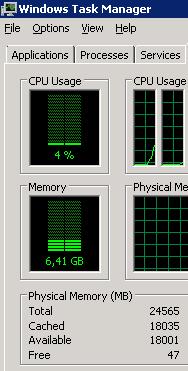
The main disadvantage of this method is that the clearing is manual and cannot be washed automatically.
Dynamic Cache Service to Manage the File Cache
Another, more than central, solution of loftier memory load past the file organization metafile is the installation of Dynamic Enshroud Service (http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=9258). This service allows to manage the parameters of the defended MFT cache using system APIs.
Important . Use this solution merely if the problem described above occurs. The installation of this service won't exist a universal solution for other causes of high retentivity usage on your servers.
It is rather easy to install DynCache (there are detailed instructions in the annal).
- Copy the file DynCache.exe to %SystemRoot%\System32 binder
- Create DynCache service using this command:
sc create DynCache binpath= %SystemRoot%\System32\DynCache.exe commencement= auto blazon= own DisplayName= "Dynamic Enshroud Service" - Import DynCache.reg to the registry (information technology contains default values)
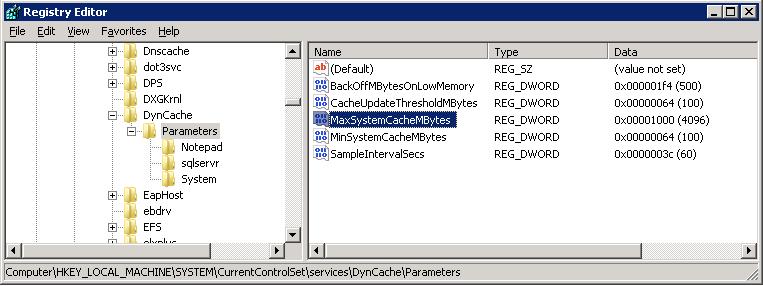
- Change the values of the following annals keys: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\DynCache\Parameters
- MaxSystemCacheMBytes: 4096 (december) – the maximum cache size(Mb)
- MinSystemCacheMBytes: 100 (december) – the minimum cache size (MB)
Note. These and other DynCache service settings have to be edited according to the RAM size, the server load, required performance, etc. As a rule, it is not recommended to set the cache size more than than one-half of the concrete RAM installed on the server. Afterwards the changes are made, you don't need to restart DynCache, since all changes are practical dynamically.
- Run the service using this command:
sc start DynCache
In our case, after DynCache service had been installed, the use of retention past the metafile stopped getting over 4 GB we had set. The users accept not reported whatsoever performance issues on the file server.
Source: http://woshub.com/fixing-high-memory-usage-by-metafile-on-windows-server-2008-r2/
Posted by: bouchertwor1982.blogspot.com


0 Response to "How To Clear Cache Memory In Windows Server 2008"
Post a Comment